Integrating Excel with Access (SQL, ADO & DAO methods)
To create Excel object using LateBinding
Automate creation of Workbook, worksheets, setting range and moving
cells
Retrieve data from Access database to Excel sheets (DAO)
Retrieve data from Access database to Excel sheet (ADO & SQL)
Export data from Excel to Access database (DAO)
Table of ADO Recordset
Properties
Export data from Excel to Access (ADO)
Add record from Excel sheet to Access (ADO & SQL)
Execute queries in Access database from Excel VBA Module
(ADO & SQL)
Execute queries and Macros, and add recordsets in Access Table from
Excel VBA (ADO & SQL)
I
f you handle tens of thousands of records in Excel, especially when you have complex formula computation in it, you easily realize the slow-down in performance as you approach mid-way to 65336 rows, and that will be the time you would want to consider utilizing the advantage of Access Multidimensional Database (MDB). Of course, the Share Workbook feature in Excel does offer you an option of multi-user access even when you don’t have massive volume of records, but there are some basic reasons you would want to avoid sharing a workbook on a network. I am not a fan of Share workbook for the obvious reasons I can not use such beautiful features like pivot tables, group and outline, Insert column, Insert worksheet, auto subtotals, styles and many others. One of the great advantages of using Access database file as a back end is that you can use deploy Excel VBA as front end to read and write from MDB file to multi-users who do not have Microsoft Access installed in their computers.When you want to copy data to or retrieve data from an Access database in Excel or Word, there are two different methods you can do this – DAO method and ADO method. DAO (Data Access Objects) works only with databases that are Jet Engine based such as Access or FoxPro. ADO (ActiveX Data Objects) is more popular, more flexible because you can deploy code that is written for say MS Access to another (say Oracle). DAO and ADO libraries both have a Recordset object, but with different methods, properties, and options. DAO is the native Access library (what Access itself uses), whereas ADO is a more generic library (now superseded by the vastly different ADO.NET library)
The starting point of any Excel automation is you need the Excel Application object to use other objects in Excel. The only risk is if you use a different version of Excel than the other users using the application.
Public Sub GetExcel_earlyBinding()
Dim xlApp As Excel.Application
Set xlApp = New Excel.Application
xlApp.Visible = True
End Sub
To eliminate the above problem, use LateBinding. That means you create
a variable as object instead of specifying an exact object type, and use Createobject to
produce the required object.
Public Sub GetExcel_LateBinding()
Dim xlApp As Excel.Application
Set xlApp = CreateObject("Excel.Application")
xlApp.Visible = True
End Sub
To create a new workbook (Add method) and save, there are 3 choices - Save, SaveAs, SaveCopyAs. The SaveCopyAs is
useful if you want to save the workbook in its current state (or with a different name) but
continue to work with the original.
Public Sub NewWorkbook_AddMethod()
Dim xlApp As Excel.Application
Dim xlWb As Excel.Workbook
Set xlApp = New Excel.Application
xlApp.Visible = True
Set xlWb = xlApp.Workbooks.Add
' to open, use Set xlWb =xlApp.Workbooks.Open("D:\Test.xls")
xlWb.SaveAs "C:\Test.xls" ' save into your default file location.
End Sub
Public Sub AddNewSheetNewRangeOffset()
Dim xlApp As Excel.Application
Dim xlWb As Excel.Workbook
Dim xlWs As Excel.Worksheet
Dim xlRng As Excel.Range
Set xlApp = New Excel.Application
xlApp.Visible = True
Set xlWb = xlApp.Workbooks.Add
Set xlWs = xlWb.Worksheets.Add
xlWs.Name = "MySheet1"
Set xlRng = xlWs.Cells(2, 4)
With xlRng
.Value = "MyCell"
.Font.Bold = True
.BorderAround.xlcontinue , xlThick, 5
End With
xlWs.Columns(xlRng.Column).AutoFit 'or columns(4)
End Sub
DAO (Data Access Objects)
DAO allows you to access and manipulate data in local or remote databases, and to manage databases, their objects, and their structure. DAO supports two different database environments, or "workspaces".
▪ Microsoft Jet workspaces allow you to access data in Microsoft Jet databases, Microsoft Jet-connected ODBC databases, and installable ISAM (Indexed Sequential Access Method) data sources in other formats, such as Paradox and Lotus1-2-3.
▪ ODBCDirect workspaces allow you to access database servers through ODBC (Open Database Connectivity), without loading the Microsoft Jet database engine.
You use Microsoft Jet workspace when you open a Microsoft Jet database (.mdb file) or other desktop ISAM database, or when you need to take advantage of Microsoft Jet's unique features, such as the ability to join data from different database formats. The ODBCDirect workspace provides an alternative when you only need to execute queries or stored procedures against a back-end server, such as Microsoft SQL Server. In this section, I will only explain on accessing Microsoft Jet database using DAO and ADO methods.
You need to set a reference to the Microsoft DAO 3.6 Object Library in order to get the DAO model to work. If you have set a reference to the ADO library you might want to uncheck that because the two models are fairly similar and it can cause some confusion if Excel calls a function from the wrong library.
|
|
Retrieve data from Access
database to Excel (DAO method)
If you want to extract certain data from an Access table to your Excel
worksheet, example 1.1 using a DAO model shows you how this can be done:
Example 1.1
Sub AccessDataToExcel_DAO()
Dim Db As Database
Dim rs As Recordset
Dim path As String, sSQL As String
Dim iCount As Long
Dim i As Long, j As Long
Dim rDest As Range
' Set the path to your database, change to suit!
path = "C:\customers\OF.mdb"
' Open the database.
Set Db = Workspaces(0).OpenDatabase(path)
Set rs = Db.OpenRecordset("AMSEA", dbOpenTable)
' Define your query - for example:
sSQL = "select Location, Customer, Material " & "from
AMSEA " & _
"where Location = '8800';"
' Open a recordset in the database (this is basically your query) and store the data in the object variable rs.
Set rs = Db.OpenRecordset(sSQL)
' Determine the number of found records
rs.MoveLast
iCount = rs.RecordCount
' Write the data from the database and insert to the worksheet
Set rDest = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A1")
If Not rs.EOF Then
rs.MoveFirst
For i = 1 To iCount
For j = 0 To rs.Fields.Count - 1
rDest(i, j + 1).Value = rs.Fields(j).Value
Next j
rs.MoveNext
Next i
End If
' Tidy up
Set rs = Nothing
Set Db = Nothing
End Sub
Retrieve data from Access database to Excel sheet using ADO & SQL
Below example shows how you can use ADO and SQL methods to filter and retrieve a table from Access to Excel spreadsheet. First, my procedure creates a connection the Access database and using DoCmd Object to execute a macro in the database. The macro runs the queries, populates the tables and export the tables to an excel spreadsheet in same folder where your database file is. For the purpose of this topic, my code only demonstrates to you how you can use SELECT FROM WHERE query statement in SQL to ‘filter’ and export the data you want from Access database to the active Excel worksheet. You can DOWNLOAD this procedure with the worksheet examples and the database file.
Example 2.4
Option Explicit
Global oApp As Object
' make VBE reference to the your latest ActiveX Objects Library
Sub GetAccessDataToExcel_ADO()
Dim Db As ADODB.Connection
Dim rs As ADODB.Recordset
Dim path As String, sSQL As String
Dim iCount As Long
Dim i As Long, j As Long
Dim rDest As Range
' connect to the Access database
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Set oApp = CreateObject("Access.Application")
' path to transfer .mdb file
path = "C:\Materials_Control\Site_Inventory.mdb"
' run Access Macro with DoCmd Object
oApp.OpenCurrentDataBase path
oApp.Visible = False
oApp.DoCmd.RunMacro "macro_Excess_Surplus_stocklist"
oApp.Quit
' define and open connection to the database
Set Db = New ADODB.Connection
Db.Open "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0; " & "Data Source=" & path & ";"
' define your query of SQL string, here I want only for Location '0001'
sSQL = "SELECT Location, Depot, Material, Excess_Inventory$ FROM excess_inventory WHERE Location ='0001';"
' define and open the recordset
Set rs = New ADODB.Recordset
rs.CursorLocation = adUseClient
rs.Open Source:=sSQL, ActiveConnection:=Db, CursorType:=adOpenDynamic, LockType:=adLockOptimistic, Options:=adCmdText
' determine the number of found records
iCount = rs.RecordCount
' add heading
Range("A1:D1").Value = Array("Location", "Depot", "Material", "Excess_Inventory$")
' write the data from the database and insert to the worksheet
Set rDest = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A2")
If Not rs.EOF Then
rs.MoveFirst
For i = 1 To iCount
For j = 0 To rs.Fields.Count - 1
rDest.Offset(i - 1, j).Value = rs.Fields(j).Value
Next j
rs.MoveNext
Next i
End If
' close the connection
rs.Close
Set rs = Nothing
Db.Close
Set Db = Nothing
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
When you have a
recordset object variable set, you probably want to manipulate the data
in the recordset.
The following table shows some commonly used methods you can use to move
through the records in a recordset.
| Method | Description |
| MoveFirst | Moves to the first record in a recordset |
| MoveLast | Moves to the last record in a recordset |
| MovePrevious | Moves to the previous record in a recordset |
| MoveNext | Moves to the next record in a recordset |
There are
wo important things to remember when working with the SQL Like clause:
1) be sure to use single and not double quotes 2) For Microsoft Access,
the wild card character is "%" and not "*".
For example, to select ‘Location’ from the Table ‘excess_inventory’ that
begin with "000", use the following SQL statement:
SELECT
Location, Depot, Excess_Inventory$ FROM excess_inventory WHERE
Location
LIKE
'000%'
For example,
if you want to display two fields concatenated together, like "PartNumber,
PartDescription", You can use a calculated expression in the SQL
statement of the query like the following:
SELECT
SalesType, PartNumber, PartDescription, PartNumber + ', ' +
PartDescription AS _
FullPartName
FROM
Sales_Records
ORDER BY
PartNumber, PartDescription
There are several
ways you can reference a table (or range) in an Excel workbook:
Use the sheet name
followed by a dollar sign, for example, [Sheet1$]. A workbook table that
is referenced in this manner consists of the entire used range of the
worksheet.
oRS.Open "SELECT * FROM [Sheet1$]",
oConn, adOpenStatic
Use a range with a
defined name (for example, [Table1]).
oRS.Open "SELECT
* FROM
Table1", oConn, adOpenStatic
Use
a range with a specific address (for example, [Sheet1$A2:H100]).
oRS.Open "SELECT
* FROM
[Sheet1$A2:H100]", oConn, adOpenStatic
|
|
Export data from Excel to Access database (DAO method)
If you want to export data to an Access table from your Excel worksheet,
the example below using DAO is one way how this can be done. Similarly,
you must add a reference to the DAO object library in your VBA project.
Example 1.2
Sub ExcelDataToAccess_DAO()
' exports data from the active worksheet to a table in an Access database
Dim db As Database, rs As Recordset, i As Long
Set db = OpenDatabase("C:\customers\UMC.mdb")
' open the database
Set rs = db.OpenRecordset("Membranes", dbOpenTable)
' get all records in a table
i = 2 ' the start row in the worksheet
Do While Range("C" & i).Value > 0
' repeat until first empty cell in column C
With rs
.AddNew ' create a new record
' add values to each field in the record
.Fields(0) = Range("A" & i).Value
.Fields(1) = Range("B" & i).Value
.Fields(2) = Range("C" & i).Value
' add more fields if you need to…
.Update ' stores the new record
End With
i = i + 1 ' next row
Loop
' close the connection
rs.Close
Set rs = Nothing
db.Close
Set db = Nothing
End Sub
ADO (ActiveX Data Objects)
ADO
Connection and ADO Recordset are the two main objects needed to access
data in .mdb file. ADO Connection defines the path and specifies that
the connection to be based on Microsoft Jet Engine. Then you use that
connection to define a recordset. A recordset can be a table, or a
subset of records in the table, or a pre-defined query in Access
database. To open a recordset, you have to specify the connection with a
query of SQL and also the values for the
CursorLocation,
CursorType,
LockType,
and the
Options
parameters.
If you have a small
dataset and with only two or few users that need to access the tables,
it may be faster to chose adUseClient for the CursorLocation. For
large datasets, you may want to use adUseServer value of the
CursorLocation property as it will free up your RAM for other tasks
while database server will process the records. adUseServer is
the default property.
The ADO Recordset object has many properties and methods that can allow
you to move through a recordset, sort, filter, find, update data
contained with the recordset. The following table gives the explanation
on the most commonly used ADO Recordset Properties used with Jet, and
the Locking Options.
| Cursor Type | Description |
| adOpenUnspecified | Does not specify the type of cursor. |
| adOpenKeyset | Keyset cursors. Recordset is fully updateable, but you records that are added by other users and deleted records are not accessible. |
| adOpenStatic | Recordset is a read-only static cursor. It generates a static list of rows at the point in time it is executed. You can move forward and backward through result sets. If another user changes a record in your cursor you won't see the change. |
| adOpenDynamic | Dynamic cursors. It shows changes that other users make and allow you move forward and backward. |
| adOpenForwardOnly | It is read-only, and can only go forward through the rows. This gives best performance if you need to go through the records quickly. |
| adLockOptimistic | Use optimistic locking where the recordsets are locked only when the record is saved. adLockOptimistic lock type is typically your best choice when deciding on a table lock for a non-read-only situation, and use it with adLockReadOnly. |
| adLockPessimistic | Use pessimistic locking where the recordset is locked when it is first edited. |
| adLockReadOnly | Lock and block you from making any changes to the entire recordset in the table. |
|
|
Export data from Excel to Access – ADO using .AddNew
Example 2.1 below using ADO method shows you how you can add records to
Access table from data in an Excel worksheet. You use the AddNew
method for the recordset. You specify the range to loop through and use
the Update method to make changes to the database. When you go
through all the following ADO examples, make sure your VBA project has
added a reference to the ADO object library. For VB 6, it is Microsoft
ActiveX Data Objects 2.8 Library. You
can also
DOWNLOAD
this example.
Example 2.1
Sub
GetExcelDataToAccess_ADO()
' exports data from active worksheet to a table in an Access database
Dim cn As ADODB.Connection, rs As ADODB.Recordset, i As Long, lastrow As Long
' connect to the Access database
Set cn = New ADODB.Connection
'define and open a recordset from the specified database
path and database table name. Change it to suit your need.
cn.Open "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & " Data Source=C:\Spares\Planning\SSLChangeRecord.mdb;"
Set rs = New ADODB.Recordset
rs.Open "SafetyStockLevel_ChangeRecord", cn, adOpenKeyset, adLockOptimistic, adCmdTable
lastrow = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count
For i = 2 To lastrow ' start from row 2 in the worksheet
With rs
.AddNew ' create a new record
' add values to each field in the record
.Fields("Date_Changed") = Range("A" & i).Value
.Fields("Part_Number") = Range("B" & i).Value
.Fields("Part_Description") = Range("C" & i).Value
.Fields("Std_Cost") = Range("D" & i).Value
.Fields("Months_Used") = Range("E" & i).Value
.Fields("Old_SSL") = Range("F" & i).Value
.Fields("New_SSL") = Range("G" & i).Value
.Fields("Reason") = Range("H" & i).Value
.Fields("Change_By") = Range("I" & i).Value
.Fields("Request_By") = Range("J" & i).Value
.Update ' stores the new record in Table Plant8800_TSLChangeRecord
End With
Next i
' close the connection
rs.Close
Set rs = Nothing
cn.Close
Set cn = Nothing
End Sub
You can use either of the following methods of ADO connection to an Excel 97 (or Excel 2000 to 2003) workbook or to a database file:
Dim oConn As New ADODB.Connection
myPath = "C:\Spares\Planning\SSLChangeRecord.mdb"
With oConn
.Provider = "Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0"
.Open myPath
' your code here....
.Close
End With
-or-
Dim oConn As New ADODB.Connection, myPath as String
oConn.Open "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & "Data Source=C:\Spares\Planning\data_upload.xls;"
oConn.Close
|
|
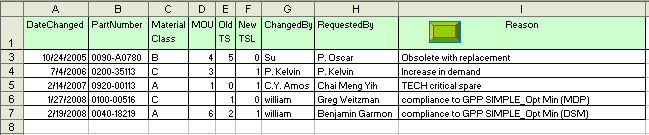
Add record from Excel sheet
to Access (ADO and SQL)
Below Example 2.2 exports a dynamic data range from Excel spreadsheet
into Access database, using an ADO connection to pass SQL strings. This
example does not insert rows if all cells in the row are blank. It will
roll back all transactions if the full update is not successful and thus
saving you time to clean up any incomplete record set. Note that all
values from Excel are passed as text strings to the mdb file and
Microsoft Access automatically converts them to the proper format.
Remember to format your Table Fields structure to the correct data type.
'7/4/2006','0200-35113','C','3','0','1','P.kelvin','P.Kelvin','Increase in demand')
'1/27/2008','0100-00516','C','0','1','0','william','Greg Weitzman','compliance to GPP SIMPLE_Opt Min (MDP)’
The transaction methods manage transaction processing during a session defined by a Workspace object as follows:
BeginTrans |
begins a new transaction. |
CommitTrans |
ends the current transaction and saves the changes. |
RollbackTrans |
ends the current transaction and restores the databases in the Workspace object to the state they were in when the current transaction began. |
Typically, you use transactions to maintain the integrity of your data when you must both update records in two or more tables and ensure changes are completed (committed) in all tables or none at all (rolled back). For example, if you transfer money from one account to another, you might subtract an amount from one and add the amount to another. If either update fails, the accounts no longer balance. Use the BeginTrans method before updating the first record, and then, if any subsequent update fails, you can use the Rollback method to undo all of the updates. Use the CommitTrans method after you successfully update the last record.
Option Explicit
' You must make reference to ActiveX Data Objects Libary
Sub AddRecord2DB_use_ADOSQL()
Dim cn As New ADODB.Connection, rs As New ADODB.Recordset, _
Path As String, TableName As String, RngHeadings As Range, RngRecords As Range, _
StrHeading As String, StrRecord As String, j As Integer, i As Integer, _
notNull As Boolean, LastColumn As Integer, LastRow As Long, LastCell, lastcellRow1
' Find the last cell in used range and last cell in row 1
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(Cells) > 0 Then
LastRow = Cells.Find(What:="*", After:=[A1], SearchOrder:=xlByRows, _
SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Row
LastColumn = Cells.Find(What:="*", After:=[A1], SearchOrder:=xlByColumns, _
SearchDirection:=xlPrevious).Column
LastCell = Cells(LastRow, LastColumn).Address
lastcellRow1 = Range("IV1").End(xlToLeft).Address
End If
' Set the string to the path and table name of your
database
Path = "C:\Planning\TSLChangeRecord.mdb"
TableName = "TSLChangeRecord_plant8800"
Set RngHeadings = ActiveSheet.Range("Sheet1!$A$1:" & lastcellRow1 & "")
Set RngRecords = ActiveSheet.Range("Sheet1!$A$2:" & LastCell & "")
' Concatenate a string with the names of the column headings
StrHeading = " ("
For j = 1 To RngHeadings.Count
StrHeading = StrHeading & RngHeadings.Columns(j).Value
Select Case j
Case Is = RngHeadings.Count
StrHeading = StrHeading & ")"
Case Else
StrHeading = StrHeading & ","
End Select
Next j
' Open database connection
cn.Open "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & "Data Source=" & Path & ";"
' Transaction processing
On Error GoTo EndUpdate
cn.BeginTrans
' Set a row counter for i
For i = 1 To RngRecords.Rows.Count
' Open the record string for concatenation
notNull = False
StrRecord = "('"
' Evaluate field in the record
For j = 1 To RngHeadings.Count
Select Case RngRecords.Rows(i).Columns(j).Value
' If record is empty, append value of 0 to string
Case Is = Empty
Select Case j
Case Is = RngHeadings.Count
StrRecord = Left(StrRecord, Len(StrRecord) - 1) & "0)"
Case Else
StrRecord = Left(StrRecord, Len(StrRecord) - 1) & "0,'"
End Select
' If record is not empty, set notNull to true, and append value to string
Case Else
notNull = True
Select Case j
Case Is = RngHeadings.Count
StrRecord = StrRecord & RngRecords.Rows(i).Columns(j).Value & "')"
Case Else
StrRecord = StrRecord & RngRecords.Rows(i).Columns(j).Value & "','"
End Select
End Select
Next j
' If record has only Null values, do not insert it to table, otherwise insert record
Select Case notNull
Case Is = True
rs.Open "INSERT INTO " & TableName & StrHeading & " VALUES " & StrRecord, cn
Case Is = False
End Select
Next i
EndUpdate:
' Check if error was encounted
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
' If rrror encountered, rollback transaction and inform user
On Error Resume Next
cn.RollbackTrans
MsgBox "There was an error. Update was not succesful!", vbCritical, "Error!"
Else
On Error Resume Next
cn.CommitTrans
End If
' Close ADO objects
cn.Close
Set rs = Nothing
Set cn = Nothing
On Error GoTo 0
End Sub
I added a form where users can chose to select Load worksheet record
data into Access table, Clear existing data on the record sheet, or to
exit the user form. You can
DOWNLOAD this procedure with
the worksheet example and the database file. Password for loading the
data is “dobeman”. Change to whatever you
like.
‘ Insert into a module
Private Sub frm_Initiliaze()
Load UserForm1
UserForm1.Show
End Sub
‘ Insert into a module
Sub clear_data()
ActiveSheet.Range("A2", ActiveSheet.Range("A2").End(xlDown). _
End(xlToRight)).Select
Selection.Clear
End Sub
‘ Click event code in your userform
Private Sub cmdLoad_click()
Dim pwd As String
Do
pwd = InputBox("enter password to open this workbook:", "password in characters")
If pwd = vbNullString Then
MsgBox "you had not entered the password"
End If
Loop While pwd <> "dobeman"
Call AddRecord2DB_use_ADOSQL
MsgBox "upload to database successful!"
End Sub
‘ Click event code in your userform
Private Sub cmdClear_Click()
If MsgBox("this will clear all data. Are you sure?", vbYesNo, "Warning") = vbYes Then
clear_data
Else
Exit Sub
End If
End Sub
‘ Click event code in your userform
Private Sub cmdHide_Click()
UserForm1.Hide
End Sub
|
|
Execute queries in Access database from Excel VBA Module
Sub RunAccessQuery()
Dim cn As ADODB.Connection
Dim strPathToDB As String, strQuery As String
strPathToDB = "C:\TSL_Change_Record\TSLChangeRecord.mdb"
Set cn = New ADODB.Connection
With cn
.Provider = "Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0"
.ConnectionString = "Data Source=" & strPathToDB & ";"
.Open
End With
strQuery = "qry_generate_Excess_Inventory_List"
cn.Execute strQuery, , adCmdStoredProc
' with adCmdStoredProc specified, the corresponding SQL statement is generated
cn.Close
Set cn = Nothing
End Sub
|
|
The ADO CommandType property sets or returns a CommandTypeEnum value that defines the type of the Command object. Default is adCmdUnknown. If you do not specify the type, ADO will need to contact the provider to determine the type of the command. However, if you do specify the type, ADO will be able to process the command faster.
|
Constant |
Value |
Description |
| adCmdUnspecified |
-1 |
Does not specify the command type argument. |
| adCmdText |
1 |
Evaluates CommandText as a textual definition of a command or stored procedure call. |
| adCmdTable |
2 |
Evaluates CommandText as a table name whose columns are all returned by an internally generated SQL query. |
| adCmdStoredProc |
4 |
Evaluates CommandText as a stored procedure name. |
| adCmdUnknown |
8 |
Default. Indicates that the type of command in the CommandText property is not known. |
| adCmdFile |
256 |
Evaluates CommandText as the file name of a persistently stored Recordset. Used with Recordset.Open or Requery only. |
| adCmdTableDirect |
512 |
Evaluates CommandText as a table name whose columns are all returned. Used with Recordset.Open or Requery only. To use the Seek method, the Recordset must be opened with adCmdTableDirect. This value cannot be combined with the ExecuteOptionEnum value adAsyncExecute. |
|
|
The following procedure not only shows you how to export data from the active worksheet to a table in an Access database, but also show you using Execute and DoCmd command to execute Query and Macro in an Access database.
Example 2.3
Option Explicit
Global oApp As Object
' make your VBE reference to the ADO Object Library
Sub ExcelRunAccessQueryMacro_ADO()
' declare variables
Dim cn As ADODB.Connection, rs As ADODB.Recordset, i As Long, Lpath As String
Lpath = "C:\Spares\Planning\ZMCR003PLN.mdb"
' connect to the Access database
Set oApp = CreateObject("Access.Application")
With oApp
.Visible = True ' set False to make Access app invisible
End With
' open a recordset in a specified path
Set cn = New ADODB.Connection
cn.Open "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0; " & "Data Source=" & Lpath & ";"
Set rs = New ADODB.Recordset
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
' execute an Access Query
cn.Execute "clear_content_refTable1"
rs.Open "refTable1", cn, adOpenDynamic, adLockOptimistic, adCmdTable
' select a range in column A and B on worksheet
"template"
Sheets("template").Range("A1").Select
Range(ActiveCell, ActiveCell.End(xlDown).Offset(0, 1)).Select
i = 2 ' start from row 2, loops thru column 1 on non-empty cells
Do While Not Range("A" & i).Value = vbNullString
With rs
.AddNew ' add recordset on Two Fields in Table "refTable1" in ZMCR003PLN.mdb file
.Fields("Serial_No") = Range("A" & i).Value
.Fields("Material") = Range("B" & i).Value
.Update
End With
i = i + 1
Loop
oApp.Visible = True ' set False to make Access application invisible
oApp.OpenCurrentDatabase Lpath
oApp.DoCmd.OpenQuery "qry_generate_Excess_Inventory_List" ' run an Access Query
oApp.DoCmd.RunMacro "macro_ScorecardZMCR002_update_refTable1_StockingList" ' run an Access Macro
' close the connection to database
rs.Close
Set rs = Nothing
cn.Close
Set cn = Nothing
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
End Sub