Automating Pivot Tables
You usually create your pivot table from the Excel User Interface by choosing from Data menu item: Data>PivotTable and PivotChart Report Wizard, but you can also use VBA to create pivot table such as when you want to automate your routine summary report.
Figure 1.1 Click on
the Layout button will bring you to the Pivot Table Layout dialog as
shown in the next diagram
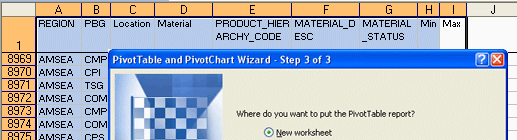
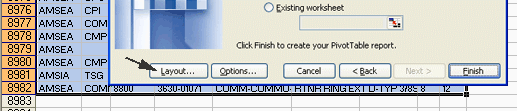
Figure 1.2 You can drag Field names from the right-hand side and
drop them in the Row, Column, and Data areas of the PivotTable and
PivotChart Report Wizard Layout dialog.
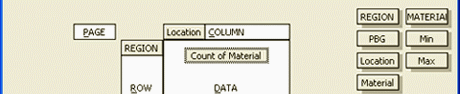
Figure 1.3
When you are done, click OK, then click Finish, and almost instantly,
Excel creates a summary of the data that you want to see.
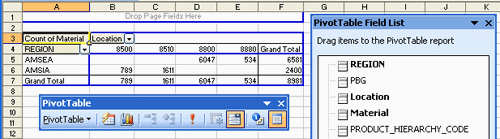
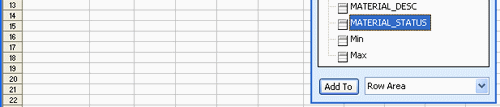
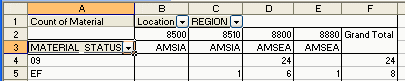
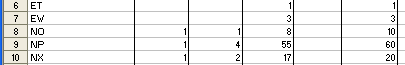
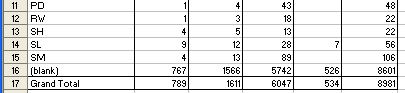
Figure 1.4 below shows another field ‘MATERIAL_STATUS’ was added to the Row area of the pivot table. You can add and remove other fields as you like to the Row, Column, and Data areas. You can move REGION to the Top, or to the Right, or to the Column, all depends on your need.
CreatePivotTable
method
The following example demonstrates an auto-creation of pivot table using VBA. In Excel 2000 and newer versions, you would first build a PivotCache object to input the data range. After the pivot table is defined, you use CreatePivotTable method to input pivot table output destination and pivot table name, and with this you create a blank pivot table based on your defined PivotCache. In the .AddFields method, you can specify one or more fields that you want to include in the Row, Column, or Data area of the pivot table. To add a field (‘Material’ as in this example) to the Page Data area of the pivot table, you would change Orientation property of the field to xlDataField.
'
Define input area and set up a pivot cache
Dim wsh As Worksheet, rng As Range, lastRow As Long, pt as PivotTable
lastRow = ActiveSheet.Cells(65536, 1).End(xlUp).Row
Set wsh = Worksheets("sheet1")
Set rng = wsh.Cells(1, 1).Resize(lastRow, 9)
' Delete any prior pivot tables
On Error Resume Next
For Each pt In wsh.PivotTables
pt.TableRange2.Clear ' TableRange2 refers to cell range of the entire pivot table
Next pt
ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Add(SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:= _
rng.Address).CreatePivotTable TableDestination:=Sheets.Add.Cells(3,
1), _
TableName:="PivotTable"
'
Set up the Row and Column fields
ActiveSheet.PivotTables("PivotTable").AddFields RowFields:="Material_Status"
_
, ColumnFields:=Array("Location", "Region")
'
Set up the Data field
ActiveSheet.PivotTables("PivotTable").PivotFields("Material").Orientation
= _
xlDataField
‘
Setting the Function property to xlSum allow you to use summation
instead of using xlCount
ActiveSheet.PivotTables("PivotTable").PivotFields("Count of
Material").Function = xlSum
‘ At
this point, if you set the ManualUpdate to False, Excel calculates. You
can immediately thereafter set it back to True
pt.ManualUpdate = False
pt.ManualUpdate = True
Here is the code:
Dim ws
As Worksheet, wsh As Worksheet, pt As PivotTable, pc As PivotCache
Dim rng As Range, lastRow As Long, wba As Workbook, wsp As Worksheet
lastRow = ActiveSheet.Cells(65536, 1).End(xlUp).Row
Set ws = Worksheets("sheet1")
Set rng = ws.Cells(1, 1).Resize(lastRow, 9)
On Error Resume Next
For Each pt In ws.PivotTables
pt.TableRange2.Clear 'TableRange2 refers to cell range of the entire
pivot table
Next
Set pc = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Add(SourceType:=xlDatabase,SourceData:=rng.Address)
Set pt = pc.CreatePivotTable(TableDestination:=Sheets.Add.Range("A3"),
TableName:="myPivotTable")
‘ To
change the orientation of the pivot fields
With pt
.PivotFields("Material").Orientation = xlDataField
.PivotFields("Region").Orientation = xlRowField
.PivotFields("Material_Status").Orientation = xlRowField
.PivotFields("Location").Orientation = xlColumnField
End With
pt.PivotFields("Region").Subtotals(1) = False
'
suppressing the subtotals for multiple column fields
pt.ColumnGrand = False
‘
suppressing the Grand Total for rows
pt.RowGrand = True '
set to False will suppress the Grand Total for Columns
Set wba = Workbooks.Add(xlWBATWorksheet)
‘
create a new workbook to hole the pivot table report
Set wsp = wba.Worksheets(1)
wsp.Name = "summary report"
‘
give the first worksheet in the new workbook a title
pt.TableRange2.Offset(1, 0).Copy ‘
use Offset(1,0) to avoid copy the title row of the pivot table
‘
copy the pivot table data to row 1 of the new report sheet
wsp.[A1].PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteFormulasAndNumberFormats
pt.TableRange2.Clear
‘
erase the original pivot table
Set pc = Nothing
‘
dissociate variable ‘pc’ from the object.
Note: if you want to
have zeros instead of blanks in the Data area of the pivot table, use
the following line:
pt.NullString = "0"
Filling in the blank Outline view in column A
If you had been using reports obtained pivot tables, you would notice this blank Outline view which are quite meaningless, usually in column A [see sample]. Here is a simple code that would let you fill in all those blank with the cell above it. See this sample output after you have executed the code.
Dim finalrow As Long
finalrow = Worksheets("summary report").Range("B65536").End(xlUp).Row
With Worksheets("summary report").Range("A3").Resize(finalrow - 2, 1)
With .SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks)
.FormulaR1C1 = "=R[-1]C"
End With
.Value = .Value
End With
The following procedure combines all the methods that I have demonstrated above on creating pivot table and different ways of moving around cells, formatting and sorting the static summary report. This diagram shot is the exact output of what you should be seeing after you run the code. You can also DOWNLOAD the worksheet sample here.
Option Explicit
' Using pivot table to create a summary report, move around cells and
formatting
Sub CreatePivotTable_SummaryReport()
Dim wsd As Worksheet
Dim pRange As Range
Dim ptCache As PivotCache
Dim pt As PivotTable
Dim finalrow As Long, finalcolumn As Long
Set wsd = Worksheets("sheet1")
'
Delete all pivot tables
For Each pt In wsd.PivotTables
pt.TableRange2.Clear
Next pt
'
Define last row, last column, input area, and set up a pivot cache
finalrow = wsd.Cells(65536, 1).End(xlUp).Row
finalcolumn = wsd.Cells(1, 255).End(xlToLeft).Column
Set pRange = wsd.Cells(1, 1).Resize(finalrow, finalcolumn)
Set ptCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Add(SourceType:=xlDatabase, _
SourceData:=pRange.Address)
Set pt = ptCache.CreatePivotTable(tabledestination:=wsd.Range("J2"), _
tablename:="PivotTable1")
'
Set up the row fields and column fields
pt.AddFields RowFields:=Array("Region", "Material_Status"), ColumnFields:="Location"
' Set
up the Data area field, set function property to Summation, format as $
in K
' Move the PivotItem object (ie. pivot field 'Stock On-Hand') to the
first position
With pt.PivotFields("Stock On-Hand")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Position = 1
.NumberFormat = "$#,##0,\K"
End With
With pt
.PivotFields("Region").Subtotals(1) = False
'
suppressing the subtotals for multiple column fields
.ColumnGrand = False ' suppressing the Grand Total for rows
.RowGrand = True
.NullString = "0"
End With
'
Calculate the pivot table
pt.ManualUpdate = False
pt.ManualUpdate = True
' Copy
data from pt.TableRange2 property to Cell S2, and wipe out the constants
that were pasted
pt.TableRange2.Offset(1, 0).Copy
Worksheets("sheet1").Cells(2, finalcolumn + 11).PasteSpecial _
Paste:=xlPasteFormulasAndNumberFormats
'
Delete original pivot table & pivot cache
pt.TableRange2.Clear
Set ptCache = Nothing
' Fill
all blanks in Outline view
Range(Range("IV2").End(xlToLeft).Address).End(xlToLeft).Offset(,
1).Select
Range(ActiveCell, ActiveCell.End(xlDown)).Rows.Offset(, -1).Select
With Selection
With .SpecialCells(xlCellTypeBlanks)
.FormulaR1C1 = "=R[-1]C"
End With
.Value = .Value
End With
'
Delete unwanted empty columns, formatting and sorting in a designated
column
Range(ActiveCell.Offset(, -1), ActiveCell.End(xlToLeft).Offset(,
2).Address) _
.EntireColumn.Delete
Range("IV2").End(xlToLeft).Offset(1, 0).Select
Range(ActiveCell, ActiveCell.End(xlDown)).Rows.Select
With Selection
.Font.Size = 11
.Font.ColorIndex = 3
.Font.Bold = True
End With
'
Autofit the selection columns
Selection.Offset(-1, 0).Resize(Selection.Rows.Count + 1,
Selection.Columns.Count _
+ 6).Offset(, -6).Select
Selection.Columns.AutoFit
' Sort
by Grand Total
Rows("1:2").Find(What:="Grand Total", SearchDirection:=xlNext).Activate
Selection.Sort Key1:=ActiveCell, Order1:=xlDescending, Orientation:=xlTopToBottom
End Sub
A note on Sort Method
It
sorts a PivotTable report, a range, or the active region if the specified range
contains only one cell.
expression.Sort(Key1, Order1, Key2, Type, Order2, Key3, Order3, Header, OrderCustom, MatchCase, Orientation, SortMethod, DataOption1, DataOption2, DataOption3)
expression Required. An expression that returns one of the objects in the Applies To list.
Key1
Optional Variant. The first sort field, as either text (a PivotTable
field or range name) or a Range object ("Dept" or Cells(1, 1), for
example).
Order1
Optional Error! Hyperlink reference not valid.. The sort order
for the field or range specified in Key1.
|
XlSortOrder can be one of these XlSortOrder constants: |
|
|
Key2
Optional Variant. The second sort field, as either text (a PivotTable
field or range name) or a Range object. If you omit this argument,
there’s no second sort field. Cannot be used when sorting Pivot Table
reports.
Type
Optional Error! Hyperlink reference not valid..
Specifies which elements are to be sorted. Use this argument only when
sorting PivotTable reports.
|
XlSortType can be one of these XlSortType constants: |
|
|
Order2
Optional Error! Hyperlink reference not valid.. The sort order
for the field or range specified in Key2. Cannot be used when
sorting PivotTable reports.
|
XlSortOrder can be one of these XlSortOrder constants: |
|
|
Key3
Optional Variant. The third sort field, as either text (a range name) or
a Range object. If you omit this argument, there’s no third sort field.
Cannot be used when sorting PivotTable reports.
Order3
Optional Error! Hyperlink reference not valid.. The sort order
for the field or range specified in Key3. Cannot be used when
sorting PivotTable reports.
|
XlSortOrder can be one of these XlSortOrder constants: |
|
|
Header
Optional Error! Hyperlink reference not valid.. Specifies whether
or not the first row contains headers. Cannot be used when sorting
PivotTable reports.
|
XlYesNoGuess can be one of these XlYesNoGuess constants: |
|
|
|
OrderCustom Optional Variant. This argument is a one-based integer offset to the list of custom sort orders. If you omit OrderCustom , a normal sort is used.
MatchCase
Optional Variant. True to do a case-sensitive sort; False to do a sort
that’s not case sensitive. Cannot be used when sorting PivotTable
reports.
Orientation
Optional Error! Hyperlink reference not valid.. The sort
orientation.
|
XlSortOrientation can be one of these XlSortOrientation constants. |
|
|
SortMethod
Optional Error! Hyperlink reference not valid.. The type of sort.
Some of these constants may not be available to you, depending on the
language support (U.S. English, for example) that you’ve selected or
installed.
|
XlSortMethod can be one of these XlSortMethod constants. |
|
|
DataOption1
Optional Error! Hyperlink reference not valid.. Specifies how to
sort text in key 1. Cannot be used when sorting PivotTable reports.
|
XlSortDataOption can be one of these XlSortDataOption constants” |
|
|
DataOption2
Optional Error! Hyperlink reference not valid.. Specifies how to
sort text in key 2. Cannot be used when sorting PivotTable reports.
|
XlSortDataOption can be one of these XlSortDataOption constants: |
|
|
DataOption3
Optional Error! Hyperlink reference not valid.. Specifies how to
sort text in key 3. Cannot be used when sorting PivotTable reports.
|
XlSortDataOption can be one of these XlSortDataOption constants: |
|
|